Exploring the Hidden Depths of the Internet: Understanding the Deep Web
February 12, 2023 • security

The deep web is a huge portion of the internet that is inaccessible using traditional search engines. It comprises information, websites, and databases that are not indexed by search engines and can only be accessed via the use of specialized tools such as Tor software. The deep web contains the vast bulk of the internet’s material, including court records, academic papers, library databases, and government information.
The Dark Web
The Dark Web is a subsection of the Deep Web renowned for its links to criminal activities such as drug trafficking, identity theft, and the illegal trading of firearms and other products. This section of the Deep Web is only accessible with appropriate tools, and is populated by criminals as well as law enforcement. People sometimes use the words “deep” and “dark” interchangeably, even though they don’t mean the same thing. The Deep Web is the unsearchable portion of the Internet that is not indexed by search engines, while the Dark Web is the portion of the Deep Web linked to criminal activity.
Why Explore the Deep Web and Dark Web?
Exploring the Internet anonymously has several advantages, especially for firms seeking a competitive edge by gaining insights about client behavior before their competitors. The Dark Web provides a place for genuine customer feedback, from which corporations may get important insights unavailable on the heavily controlled and filtered Clear Net. Although, the Dark Web’s ethos, which is defined by a sense of adventure and unpredictability, may provide a problem for the data-driven business world.
How is the Structure of the Deep Web Different from the Surface Web?
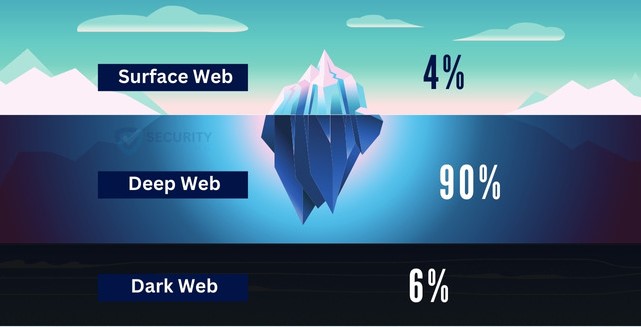
The linguistic system used by the Deep Web, TCP/IP (Transmission Control Protocol/Internet Protocol), is similar to the one used by the Surface Web. This system allows computers to communicate with each other over the Internet by transferring data in the form of network packets. The smallest unit in this system of measurement is a packet, which can be composed of bits, bytes, kilobytes, megabytes, gigabytes, or terabytes.
TCP compresses large amounts of data into manageable packets, while IP acts as a marker to help the packets reach their destination across the vast network of the Internet.
The original TCP/IP system consisted of four layers:
- The application layer
- The transport layer
- The internet layer
- The link layer
The way you interact with the Internet is through a layer called the application layer. This layer helps the communication between different websites, even if they are on the same website, two different websites, or located nearby or far away from each other. The network layer connects all these websites, and the link layer represents the physical equipment you use to access the Internet.
The Surface Web and the Deep Web have different types of website listings. Websites on the Surface Web are listed in the DNS registry and can be easily found using common web browsers like Chrome and Firefox. However, websites on the Deep Web do not show up in the DNS registry and cannot be found using regular methods.
The Origin of the TOR Project
The TOR Project, had its beginnings at the US Naval Research Laboratory. In the 1990s, Paul Syverson, David Goldschlag, and Michael Reed came up with the idea of “onion routing.” Roger Dingledine and Nick Mathewson later refined the concept and officially launched the TOR Project on September 20th, 2002. The Electronic Frontier Foundation (EFF) continued funding the project to further its development.
TOR was initially developed to protect the identities of military personnel stationed overseas. To further hide their identities and locations, TOR was released to the public in October 2003 as a free, open-source browser. The goal was to blend military personnel into the anonymous traffic of civilian users.
Understanding the Working of Tor Network
Tor, or The Onion Router, is a network consisting of thousands of volunteer routers, also known as nodes. The functioning of Tor is relatively simple. When a user’s data is sent through Tor, it is encrypted at least three times, or relays, before reaching its destination. This makes it difficult, if not impossible, to trace the user or client as their identity and address are masked three times.
Tor not only provides anonymity to individual users but also to entire websites, and it helps with the configuration of Peer to Peer (P2P) applications for sharing and downloading torrent files.
you can volunteer to be a part of it by running one of three types of nodes: middle relays, exit relays, or bridges.
- Middle relays pass along data, maintain its speed, and encrypt it. They are easy to find and relatively safe to connect to since their location is hidden.
- Exit relays are the final stop in the encryption process and are visible to everyone on the network. However, if an illegal activity takes place on the network, the exit relay may be held responsible. Running an exit relay is not recommended for hobbyists or personal computer users as the police may seize your computer if it is compromised for illegal activities.
- Bridge relays on the Tor network are not listed publicly and help to avoid censorship in countries like China. They are considered safe to run in your home, similar to middle relays.
Accessing the darknet
To gain access to the darknet, special software like the Tor browser is needed. This browser helps you visit websites that aren’t indexed by regular search engines and provides increased privacy and anonymity.
Before accessing the darknet, it’s highly advisable to set up a Virtual Private Network (VPN) first. Setting up a VPN is crucial for protecting your online privacy and security. With a VPN, your internet traffic is encrypted, making it difficult for others to monitor your online activities. This means that your Internet Service Provider (ISP) won’t be able to track which websites you visit or what content you access on the darknet.
Surfing the Darknet
Once you have connected to the Tor network, you can search for websites hosted on the darkweb using a search engine such as Torch, or by manually typing in the URL of a specific website. The browser will block plugins such as Flash, RealPlayer, QuickTime and others that could be manipulated into revealing your IP address. This makes it easier to protect your identity while browsing the web. Additionally, all of your web traffic is anonymized through the Tor network, making it impossible to trace back to you.
Dark Web Search Engines
When searching for information on the dark web, it’s essential to use a secure and private search engine that allows for anonymous browsing. You also want a search engine that is fast and efficient, so you can quickly find the information you need.
Here are some of the best dark web search engines that can be used with the Tor Browser:
- Torch: Torch is a fast and efficient dark web search engine that sources its results from over 60 different platforms, including social media sites like Twitter and Reddit, and websites hosted on the Tor network. It offers advanced features like keyword highlighting and filtering options to help you find what you’re looking for quickly and easily.
- Not Evil: Not Evil is a user-friendly dark web search engine that allows you to search for specific content by using keywords or phrases. It features a variety of filters, such as language, region, date range, file size, and others, that make it easy to refine your search and find the information you need quickly.
- Ahmia: Ahmia is a Finnish-based dark web search engine that focuses on finding content related to illegal activities, such as child exploitation. It uses a combination of machine learning and human intelligence to provide accurate and up-to-date results that are not accessible through traditional search engines.
- Grams Search Engine: Grams Search Engine is a Russian-developed search engine that helps users access information about illegal goods, such as drugs and weapons, being sold in Russia. It aggregates listings from various marketplaces, making it easy to browse all the listings in one place, rather than having to visit each marketplace individually.
- Candle Light Search Engine: Candle Light is a dark web search engine that specializes in providing links to illegal businesses, such as those selling drugs, weapons, and stolen credit card data. It focuses solely on giving links to these businesses, rather than indexing product listings, which provides improved security as there is no need to worry about third-party tracking.
Law Enforcement vs. the Darknet: The Ongoing Battle
Law enforcement and the darknet have long been in an intense battle of cat-and-mouse. With its anonymity and lack of regulation, the darknet has become a popular destination for criminals to carry out nefarious activities such as purchasing drugs or weapons, making it increasingly difficult for law enforcement agencies to catch them.
As a result, these organizations must be creative when tracking down perpetrators on this mysterious network; they employ sophisticated methods designed specifically to pick up even the most inconspicuous criminal activity occurring within its depths.
- One way law enforcement has been able to crack down on illegal activity on the darknet is by using advanced analytics tools that allow them to analyze large amounts of data quickly and accurately. These tools help them find patterns in how users act, which could be signs of suspicious behavior or even links between people who are doing illegal things.
- Another technique used by law enforcement is undercover operations, where agents pose as buyers or sellers on various marketplaces within the darknet in order to gather evidence against those involved with illicit activities online. This type of operation requires a great deal of skill and training from agents, as they must be able to blend into their environment without arousing suspicion from other users while still gathering enough information about potential suspects or targets before making any arrests or seizures related to criminal activity taking place on the network itself.
- Lastly, some countries have started to pass laws that go after people who do illegal things through online networks like Tor, which is the most popular browser used to get to sites on the Dark Web. For example, many European countries now require internet service providers (ISPs) to report any suspicious traffic coming from Tor-based services, which can then be investigated further by police forces if necessary.
Ethics and morality
The dark web is the dark and hidden part of the internet, used for illegal activities such as drug trafficking and money laundering. However, it also has its own set of ethics and morality that govern interaction.
When discussing dark web ethics, both criminal activities and privacy seekers must be considered. Some may argue that buying drugs or weapons is unethical due to law-breaking, while others may argue for privacy rights, even if laws are broken.
Cryptocurrencies, such as Bitcoin, can anonymize dark web transactions but also have potential for misuse, such as facilitating money laundering.
Given its association with criminal activity, one must question the morality of actions taken on the dark web. Anonymity may provide safety for victims of oppression or whistleblowers, but can also enable organized crime and terrorism.
The debate on what constitutes “right” versus “wrong” behavior on the dark web will likely continue due to a lack of expert consensus. Despite the risks, many still use the dark web for privacy protection and to avoid cybercrime.
It is up to individual users to determine the ethics of their actions on the dark web based on their personal digital ethics.
Future of the darknet
The future of the dark web is uncertain and open to speculation. On one hand, increased efforts by law enforcement and government agencies to crack down on illegal activities could result in a safer and more regulated dark web. On the other hand, privacy concerns and the increasing use of technology may lead to an expansion of the dark web as a haven for illegal activities.
In conclusion
The dark web is complex with both illegal and privacy-protective uses. Its future is uncertain and influenced by technology and various stakeholders. It is important to stay informed for a secure online environment.
security
admin is a senior staff writer for Government Technology. She previously wrote for PYMNTS and The Bay State Banner, and holds a B.A. in creative writing from Carnegie Mellon. She’s based outside Boston.