understanding access control systems
October 07, 2022 • César Daniel Barreto

The ultimate objective of any security system is to provide individuals and organizations with a sense of safety. When a group has complete control over its assets and can utilize them without restriction, this utopia comes into being. People can enjoy genuine peace of mind when they do not have to worry about losing access or ownership.
Constantly being on the lookout for new cyber attacks is a full-time job for cyber security experts. These specialists can never let their guard down, as new types of cyberattacks are constantly developed.
Security can be considered the degree to which measures are taken to protect against potential damage. The goal for any company or organization would be to keep their system’s security level high enough so that only authorized personnel are allowed access while also protecting them from outside threats like hackers who may try stealing information through cyber-attacks.
Cyber vs. Physical Security
The term “physical security” encompasses the measures taken to protect your property from theft or damage. Physical security may include tools like locks and gates and policies such as employee background checks. “Cyber security,” on the other hand, describes the steps taken to defend against digital threats. Cyber security includes protecting physical access to devices and systems that store data (like servers) and measures related to network security, informational access, and control of the system’s data.
Today, in order to be secure, both physical and cybersecurity must work together. To ensure everything is covered, it’s crucial to have a comprehensive security plan that encompasses all security aspects. This includes ensuring secure infrastructure (physical buildings, systems, etc.).
We tend to think about infrastructure security in terms of physical structures, such as lockable doors or windows. However, many additional aspects are involved in establishing an effective security system. These methods generally incorporate a mixture of crucial security measures devised and tested to fulfil operational and corporate demands.
The Three Layers of Physical Access Control
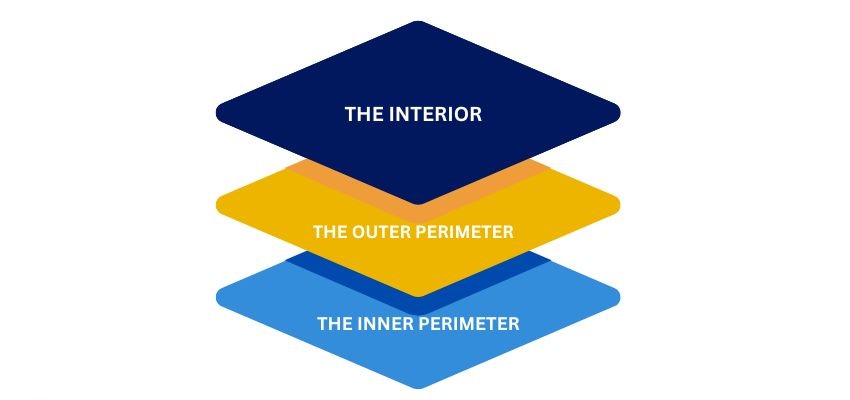
There are three general layers to developing and implementing a strategy to secure an infrastructure asset.
- The Interior This is the innermost layer of protection, which incorporates the Interior of the structure, office, cubicle, and so on that lies within the inner and outer perimeters.
- The Outer Perimeter This is the space surrounding a secure area. To secure this space, you must control who can cross the legal or physical line that marks its boundaries. For example, property lines or the exterior walls of a building would honor the outer perimeter of a complex.
- The Inner Perimeter This is Often defined by physical barriers like walls, doors, and windows—either exterior or Interior, depending on the context of the outer perimeter.
A comprehensive security plan will cover all three levels of security. The three layers of security are typically composed of various technologies that work together to form an effective physical protection solution.
Logical Perimeter Security 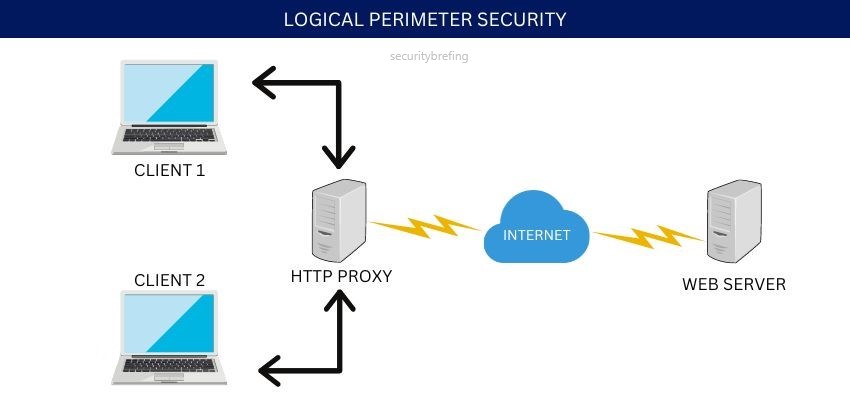
In addition to the three physical layers, there is also what’s known as logical perimeter security. This term covers the electronic access controls that are in place to protect systems and data. These include passwords, user IDs, encryption keys, and other digital means of keeping information safe.
Natural Access-Control Methods
Natural access control involves using natural design elements to restrict or allow access to an area, for example, using a river as a natural barrier to protect against ground-based attacks.
Territorial Reinforcement
Territorial reinforcement employs structures, systems, and policies to establish and maintain a physical security presence. For example, this may involve lighting to increase an area’s visibility or establishing access control measures like gates and fences.
Technological Access-Control Methods
Technological access control uses technology to restrict or allow access to an area. Include CCTV systems, alarm systems, and access control systems.
Infrastructure security operation and management are based on three basic types of subsystems:
- Deterrence
- Prevention
- Response
Deterrence is based on the idea that if an intruder knows they are more likely to be caught, they will be less likely to attempt an attack.
The goal of prevention is to make it more difficult for an intruder to access the target. This is done by making it harder to find the target, harder to approach the target, and harder to breach the target.
Response systems are designed to detect an intrusion and then take action to stop the attacker and minimize the damage they can cause.
A well-designed security system will combine all three of these subsystems to create an effective deterrent, prevention, and response system.
Access Control
The number one priority for security systems, as agreed by most experts, is to prevent intruders using deterrence. Parts of the infrastructure can be restricted so people without clearance cannot cause any damage, destruction, or theft.
Egress, or the legal right to leave a facility, is defined as the route used by people to enter and exit a place. Physical security may be defined as ingress, which refers to the physical pathway used by someone to go into a site and come out correctly.
In security terms, a right is a legal privilege or permission granted to someone or some group by a recognized authority. This authority can be a government, a legally recognized governmental agent, or the owner of an asset. When unauthorized people attempt to gain access to an asset they do not have rights to, they become intruders.
Therefore, access control is about controlling who can come into, go out of, and come back into an asset. Controlling the access of unauthorized people to essential assets is a crucial security step that you can take.
Authorization
Authorization may be the property line of the organization’s physical property or the front door of their facilities.
The main objective of a perimeter is to authorize personnel only. Different methods can be used to achieve this- like planting hedges around the property line or placing visible signs. If an unauthorized individual tries crossing, they are immediately stopped by security features such as barbed wire fencing with gates and armed guards.
Most access-control efforts occur between a property’s outer and inner perimeters. This can include having employee and guest parking in strategic places and using landscaping to direct people to specific entrances and exits and keep them away from other possible entry/exit points.
This also means keeping your home safe from intruders. You can do this by using physical barriers such as walls, windows, and doors. These barriers will keep people from getting too close to your home and help protect you and your family.
Interior security is the security of the people and things inside a building or area. This includes watching the people and also using machines to watch, track, and detect anyone who enters without permission. This system also records what happens in the area so that we can see if someone breaks the rules. Having both people and machines working together makes this type of security very effective.
Security Policies
A good security policy that explains how security works at each level is fundamental. Businesses and organizations must create comprehensive security policies explaining who is allowed to access different assets and what they can do with them. This way, everyone will know what they should do to keep everything safe.
Companies and organizations may protect their workers and equipment from accidents by taking these extra measures. They can prevent people who aren’t authorized to be in specific areas from causing damage by putting up an access control system with restrictions on where employees can go.
For example, if a sales representative inadvertently spills coffee on one of the production servers in the engineering department, that would be a significant disaster.
Businesses should develop a clear Security policy that allows authorized people to access certain assets while keeping unauthorized people from accessing those same assets.
The vital role of access control in cyber security
In the digital world, access control is just as essential as it is in the physical. Businesses must authenticate people attempting to enter their networks and limit which users have access to sensitive data or parts of the network in order to defend against external dangers. You don’t want anyone breaking into your home or office, and you don’t want such individuals gaining access to your computer systems. Hackers may obtain critical information, such as customer data or trade secrets, and wreak havoc on your company.
There are two types of access controls in the digital world:
- Physical
- Logical
Physical controls prevent users from accessing offices, workstations, and hardware, whereas logical controls protect critical cyber assets. Both are important for cybersecurity; both begin with the assumption that people attempting to enter are unknown until the system is able to confirm it by their ID, which is the username, email, or MAC address, that identifies them when they request access.
Identification and authentication
Access control ensures that only authorized individuals can enter systems and view data. To do this, businesses must be able to identify and authenticate users. Identification is the process of determining who requests access, while authentication confirms that the user is who they claim to be.
There are three types of identification methods:
- Something you know
- Something you have
- Something you are
Something you know, like a password or PIN; something you have, such as a physical token or keycard; and something you are, such as your fingerprint or iris scan. The first two can be lost or stolen, so biometrics is the most secure form of identification.
There are four types of authentication:
- Single-factor
- Two-factor
- Three-factor
- Multi-factor
Single-factor authentication uses only one type of identification, such as a password. Two-factor authentication adds a second layer, such as a security code sent to your phone. Three-factor authentication adds a third layer, such as a fingerprint scan. Multi-factor authentication combines two or more of these methods.
Software entities
In an access control system, a subject is an entity that can request access to a resource, while an object is an entity that stores or provides the resource. In most cases, subjects are users, and objects are files, programs, or devices. However, subjects can also be processes or threads that request access to an object, and objects can be Active Directory objects, such as users, groups, or computers.
There are three types of software entities in an access control system:
- Users
- Objects
- Processes
A user is a human being who interacts with the system, while an object is something that the system uses or manipulates, like a file. A process is a set of instructions that a computer carries out.
Cybersecurity professionals must be able to identify which users, objects, and processes should have access to which resources, and they must be able to implement the appropriate controls to ensure that only authorized individuals can gain access.
Computer Access control systems
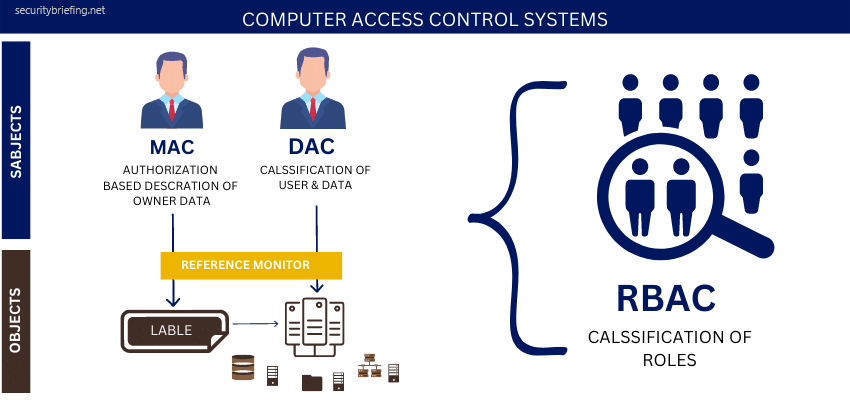
There are many types of computer systems access control systems. Still, the most common are Role-based access control (RBAC), Discretionary access control (DAC), Mandatory access control (MAC), and (HBAC) Host-based access control.
RBAC – is the simplest model, and it assigns roles to users. For example, a manager would be able to access files needed to do their job, but they wouldn’t have access to sensitive employee information. This type of system is easy to implement and maintain, but it’s not very flexible.
DAC – is a bit more complex, as it assigns access permissions to individual users. This means that each user has their own set of permissions, which can be customized according to their needs. This type of system is more flexible than RBAC, but it’s also more challenging to manage.
MAC – is the most complex type of access control system. It uses a security label to define the sensitivity of data and control who can see it. This type of system is very secure, but it’s also tough to implement and maintain.
HBAC – is a hybrid of the other three types of access control systems. It uses both roles and permissions to control access to data. This type of system is more flexible than RBAC and MAC, but it’s also more challenging to manage.
No matter which type of access control system you choose, it’s important to remember that they are all designed to protect your data and your company. Choose the one that best fits your needs, and be sure to implement it properly.
Access control is vital for both physical and digital security. By understanding the different types of access control systems, you can choose the right one for your needs and make sure that your assets are safe.
César Daniel Barreto
César Daniel Barreto is an esteemed cybersecurity writer and expert, known for his in-depth knowledge and ability to simplify complex cyber security topics. With extensive experience in network security and data protection, he regularly contributes insightful articles and analysis on the latest cybersecurity trends, educating both professionals and the public.