VPN 101
July 15, 2022 • security

Virtual Private Networks, commonly known as VPNs, play a crucial role in enhancing your online privacy by encrypting internet traffic and obscuring your digital identity. This added layer of security deters third parties from tracking your online behavior or obtaining your personal data.
The following article will delve into the intricacies of VPNs.
What is a VPN?
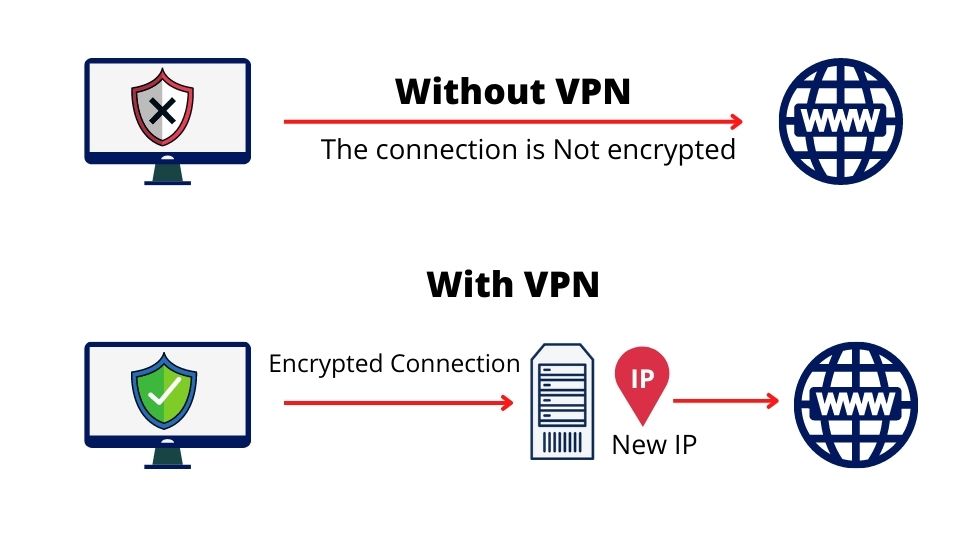
Think of a Virtual Private Network (VPN) as your personal bodyguard on the internet. This handy piece of software is all about keeping you safe and private while you surf the web. Imagine all your data safely transported inside a secure tunnel, hidden from prying eyes. To top it off, it cloaks your IP address, keeping your online identity under wraps and providing secure links to open Wi-Fi hotspots. VPNs are equipped with some pretty cool tech to ensure a secure handshake between two locations.
Let’s say you’re sitting at home and need to tap into resources on your office network – a VPN can help you with that. It’s like creating a secure, private path over the wide-open internet, which acts like a giant network. Depending on your specific needs, this secure line can provide specialized services to make your digital journey safer.
How Does a VPN Work?
Picture a VPN, or Virtual Private Network, as a secure digital pipe that connects your device with another computer anywhere across the world. All you need to set this up is your internet-connected device and the right VPN software. Inside this pipe or “tunnel”, your data is scrambled into a code that’s hard to crack, keeping it safe and private as it travels across the internet.
The Role of IP Addresses
When you connect to the internet, your device is assigned a unique identifier known as an IP address. This address reveals details about your geographical location and Internet Service Provider (ISP). A VPN replaces your IP address with one from the VPN server, hiding your real location and ISP information.
The Encryption Process
Encryption is like a secret language that only you and your device understand. It takes your data and transforms it into a cryptic format that looks like gibberish to anyone else.
To read this secret language, you need a special key – and without it, this information remains a secret. Now, some savvy VPN services take this a step further with what’s known as ‘zero-access’ encryption. In this case, even the VPN providers don’t hold the key to decode your data. It’s like putting your data in a safety deposit box that only you can open.
The Various VPN Protocols
VPN protocols determine how your device connects to the internet. Each protocol offers varying features and security levels.
The following are some of the most common VPN protocols:
- PPTP (Point-to-Point Tunneling Protocol): PPTP is an older, widely compatible VPN protocol. It’s easy to set up but lacks security.
- L2TP/IPsec (Layer 2 Tunneling Protocol combined with Internet Protocol Security): This protocol is more secure than PPTP but may be slower and more difficult to configure.
- SSTP (Secure Socket Tunneling Protocol): SSTP provides strong security and potentially faster speeds than L2TP/IPsec, but it’s only available on Windows systems.
- IKEv2/IPSec (Internet Key Exchange Version 2, coupled with Internet Protocol Security): IKEv2/IPSec is a newer, fast, secure, and user-friendly protocol supported on most devices.
VPN Technologies
Several VPN technologies are widely used today:
- OpenVPN: A reliable and secure VPN technology known for consistent performance. OpenVPN is a preferred choice for those seeking robust encryption. However, it may lack advanced features like faster browsing speeds, essential for content streaming services like Netflix or Hulu Plus.
- WireGuard: This newer open-source VPN protocol offers faster speeds and utilizes modern encryption methods. WireGuard is suitable for users seeking a compact yet reliable service.
- PPTP: An older VPN technology still in use today. Despite supporting only dial-up connections and compromised encryption, its fast performance has ensured continued popularity.
- IKEv2: A security protocol that offers protection against network threats through data encryption and authentication. IKEv2 has an advantage in speed, but its connection could abruptly switch networks, which might cause issues for users needing a rapidly updated IP address while on the move.
Importance of No-Logging Policies
No-logging policies are a crucial aspect of VPN services that further ensure your online privacy.
A VPN with a no-log policy doesn’t track your online activities or IP address. This means the VPN provider doesn’t keep any logs that record your internet activity.
Site-to-Site VPN
Site-to-site VPNs provide another dimension of secure connectivity.
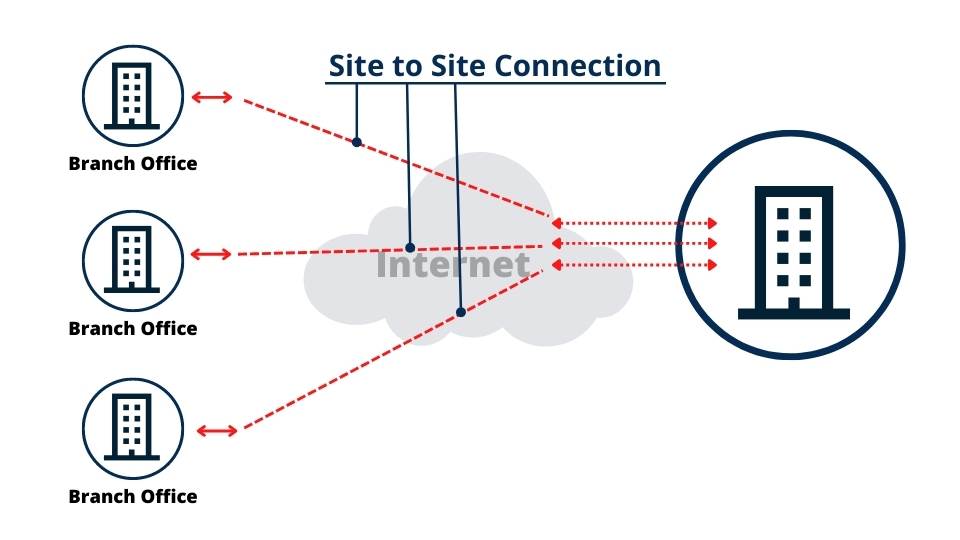
Site-to-site VPN enables users to connect to a corporate network from any location via the Internet. This feature allows access to vital network resources, such as email servers or application servers responsible for managing email or storing data.
Benefits of Site-to-Site VPN:
- Scalability: VPNs can be effortlessly scaled up or down in line with business requirements by adding or subtracting VPN servers.
- Performance: VPNs deliver high performance as each site is equipped with specialized VPN hardware.
- Stability: VPNs offer enhanced reliability and stability, unaffected by internet connection issues.
- Security: VPNs improve protection by encrypting data before transmitting it over the open internet.
Drawbacks of Site-to-Site VPN:
- Visibility: Supervising and controlling data transfers can be challenging due to the independent functioning of each site-to-site VPN connection, which might inadvertently lead to data decentralization and increased network latency.
- Security: While a site-to-site VPN can protect one location when both sites are connected to the same network, controlling access and usage of the data becomes challenging, potentially leading to suboptimal security even if it is encrypted at two separate locations.
Types of VPNs
Several types and protocols of VPNs are designed to cater to various needs. The three primary VPN categories are Remote-Access, Intranet-based Site-to-Site, and Extranet-based Site-to-Site.
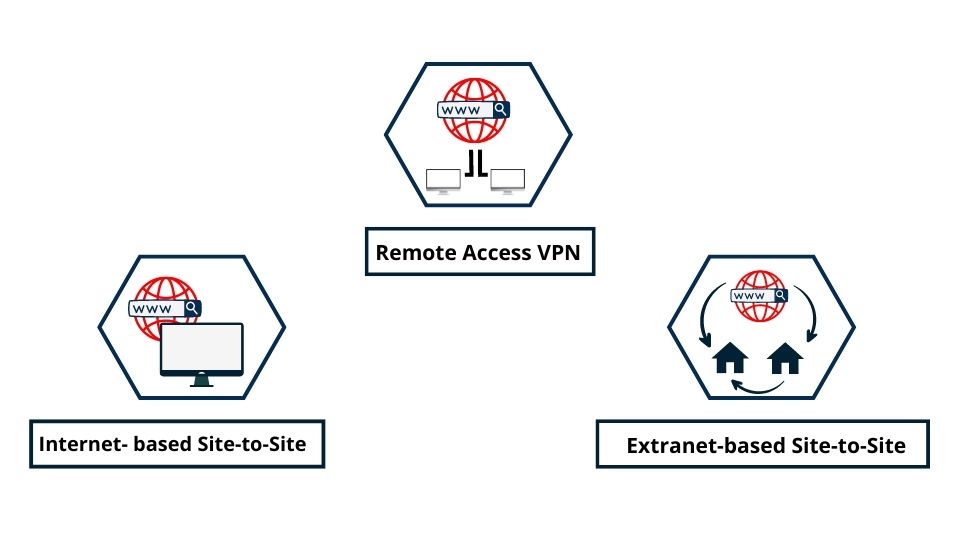
Intranet-Based Site-to-Site
An Intranet-based Site-to-Site VPN essentially unifies various local networks into one large network domain. It’s widely utilized by enterprises with multiple branches, allowing them to merge resources from various locations securely as if they were operating from a single physical site. This type of VPN configuration can also be instrumental in implementing Software-Defined WAN (SD-WAN), enhancing network management and efficiency.
The importance of a site-to-site VPN becomes evident when every location possesses unique processes or resources that the entire organisation needs access to. For instance, with an Intranet-based Site-to-Site VPN established among multiple corporate branches, each branch can access updated design blueprints customized for clients, regardless of their geographical location.
Site-to-site VPNs have been around for a long time, even predating the modern internet, due to their connection to ARPANET and the inception of Transmission Control Protocol/Internet Protocol (TCP/IP) traffic.
Remote Access VPN
A Remote Access VPN is a software program that secures connections between two networks. Users working from home can securely access corporate data center applications and data, with all traffic sent and received encrypted.
VPNs enable remote users to access a company’s network as if they were physically present. Data can be transmitted without the organization worrying about it being tampered with or intercepted. Employees working remotely can connect to a server at their desk via a remote access VPN, creating a work environment similar to that of employees at the main office with a direct connection.
Extranet-Based Site-to-Site
Extranet-Based Site-to-Site VPNs are used by organizations wanting to share specific information while preserving privacy. Each entity connects to the Extranet-Based Site-to-Site VPN and decides what information to share with other businesses. They can collaborate without compromising their intellectual property.
Extranet VPNs are commonly used to securely connect business partners to share data and applications, often using the internet as the transport medium. Extranet VPNs require special VPN gateway software at both ends of the connection to encrypt and decrypt data between the two sites.
Using VPN for Unblocking Streaming Services
Users may need to bypass VPN blocks to gain unrestricted access to geo-restricted content. Various methods can be used to evade these blocks, such as utilizing obfuscation or “stealth” servers that disguise VPN traffic as regular HTTPS traffic. Alternatively, trying a different VPN server or altering the VPN protocol can be effective.
Some users prefer using residential IP addresses over data center IP addresses to avoid being flagged by streaming services. Choosing a reliable VPN provider with robust features capable of overcoming these blocks is crucial for a smooth streaming experience.
Here are some VPNs known for unblocking streaming services:
- ExpressVPN: Known for its extensive network of servers in 94 countries, ExpressVPN can bypass geo-restrictions on platforms like Netflix, BBC iPlayer, and Hulu.
- NordVPN: With servers in 62 countries, NordVPN can unblock Netflix, BBC iPlayer, Hulu, and more.
- CyberGhost VPN: CyberGhost VPN, with servers in 60 countries, can bypass geo-restrictions on Netflix, BBC iPlayer, Hulu, and more.
- PrivateVPN: This is another excellent option for unblocking streaming services. PrivateVPN has a network of servers in 50 countries and can unblock various streaming platforms.
How to Use a VPN
Using a VPN is a straightforward process, applicable at home or on the go. Here’s a step-by-step guide to setting up and using a VPN across your devices.
- Choose a VPN Service: Start by choosing a good one offering an extensive server network across multiple locations, no logging policies, and robust encryption.
- Download and Install the VPN App: After choosing a service, download and install the VPN application on your device.
- Sign in and Select a Server Location: Open the VPN app and sign into it using your credentials.
- Select a server location based on your needs: For instance, if you wish to watch US Netflix, you would connect to a server located in the United States.
- Connect to a Server: Look for a quick connection option in your favorite apps. If there isn’t one, research the best server based on your wireless or wired connection’s traffic to ensure optimal performance during the connection.
VPN Configuration
You’ll be asked to sign in with your account upon downloading a VPN app. Before using it on public networks like airports or coffee shops, review each program’s settings to ensure they match your preferences.
Configure VPN on iPhone or iPad
- Download and install the VPN app. When prompted to allow the app access while creating a new connection, click “Allow” for automatic setup.
- Once the VPN is enabled, go to “Settings“.
- Tap “General“.
- Select the VPN app.
- Toggle the “Status” switch on.
Configure VPN on Android Devices
Android devices are versatile tools, and protecting your online activity is crucial. To connect your Android device with a VPN, follow these steps:
- Download and install a VPN app from the Google Play Store.
- Sign in.
- Choose a server.
- Tap “Connect“.
Configure VPN on Windows PC
To connect your PC with a VPN, follow these steps:
- Click on the Windows logo and go to “Settings“.
- Choose “Network & Internet“, then “VPN“.
- Fill in the connection settings: Select “Add a VPN Connection” from the drop-down list and add your VPN connection. Fill out the login details correctly and click “Save”.
- After selecting a VPN connection from the VPN Settings screen, click “Connect”.
Configure a VPN on Mac
Mac users can utilize the built-in settings to set up a VPN. Have all the necessary information ready, including the type of VPN (PPTP vs. L2TP), server address/name, username, password, and shared secret. This information is unique for each network provider; you should get it from them before setting it up.
- Click the Apple logo, then “System Preferences“.
- Click “Network“.
- Click the Plus key to create a new network.
- Enter the Server Address and the Account Name, then click “Authentication Settings”.
- Enter the Password, then the Shared Secret, and click “OK“.
- Click “Apply“, then “Connect”.
Summary
VPNs are potent tools for ensuring online security and privacy. They establish a secure, encrypted connection between your device and a remote server, allowing for anonymous browsing and data protection. By masking users’ IP addresses, VPNs help bypass geo-restrictions and guard against government scrutiny and unwanted surveillance.
As they are compatible with smartphones, tablets, and laptops, it’s crucial to evaluate each VPN based on its security, speed, server locations, and privacy capabilities to ensure the best experience.

security
admin is a senior staff writer for Government Technology. She previously wrote for PYMNTS and The Bay State Banner, and holds a B.A. in creative writing from Carnegie Mellon. She’s based outside Boston.