Remote Attack
September 15, 2022 • security

What is a Remote Attack?
When a thief robs a house for material items, they risk leaving DNA evidence or fingerprints that could lead to their arrest. However, hackers who commit cyber crimes can do so without ever being in the same vicinity as their victim and therefore are much less likely to be caught. In addition, experienced hackers can frame innocent people by planting false evidence online that points back to the innocents’ digital devices or accounts.
As experienced hackers are skilled in finding weaknesses in current systems, none of the preventative tools or methods can stop them. Unfortunately, those responsible for developing legal measures to protect people and businesses from hacking do not appear to be truly knowledgeable or concerned about it themselves.
Types of Remote Attacks
Attackers can take control of remote systems in diverse ways:
DNS Poisoning
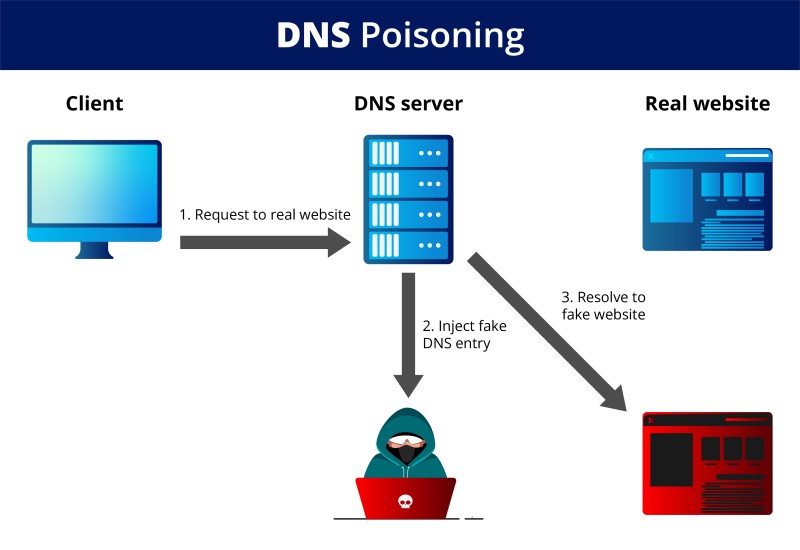
Every device and server has a set of numbers called an internet protocol (IP) address used to identify it in communications. Each website has a domain name to help people find the websites they want (e.g., www.domain.com). The domain name system (DNS) converts the user-specified domain name into the correct IP address using DNS servers to route traffic appropriately. All of this is managed through DNS servers.
DNS poisoning is when an attacker reroutes traffic from the intended website to a fake site by changing DNS records. For example, if you try to log into your online banking account, but instead you get redirected to a page that looks identical to the bank’s login page, the attacker has performed a DNS poisoning attack. If you enter sensitive information into this fake website, the attacker can steal your information for their benefit.
Port scanning
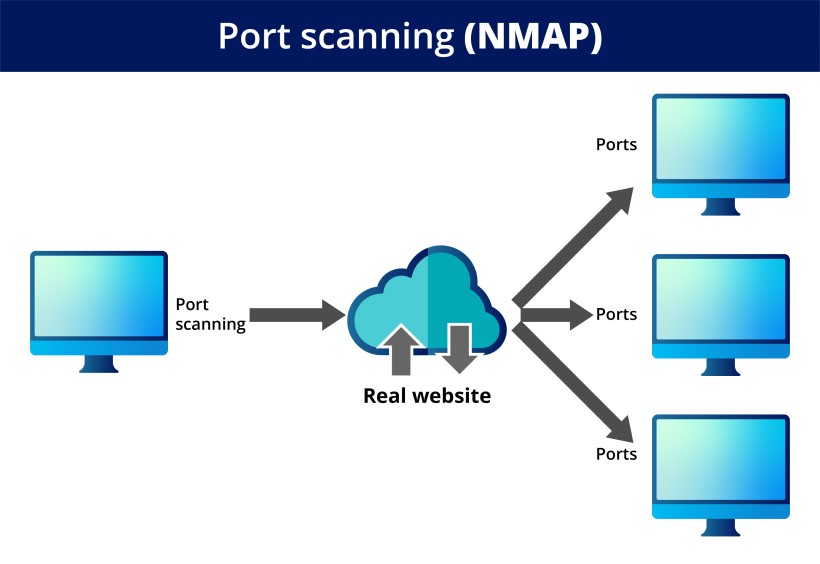
Port scanning is a way of finding out which ports on a network are open. This is done by trying to send and receive data through each port, like knocking on doors to see if anyone is home. If someone answers, you know that the port is open. They run a port scan against a network or server to show which ports are open and listening (receiving information) and whether security devices like firewalls exist between the source and target. Port scanning can also be used to fingerprint a device by looking at the activity of individual ports.
This program is not only used by Security admins to monitor their network for any vulnerabilities, but it is also often used by hackers as part of their reconnaissance when looking for weak points to exploit.
DoS attacks
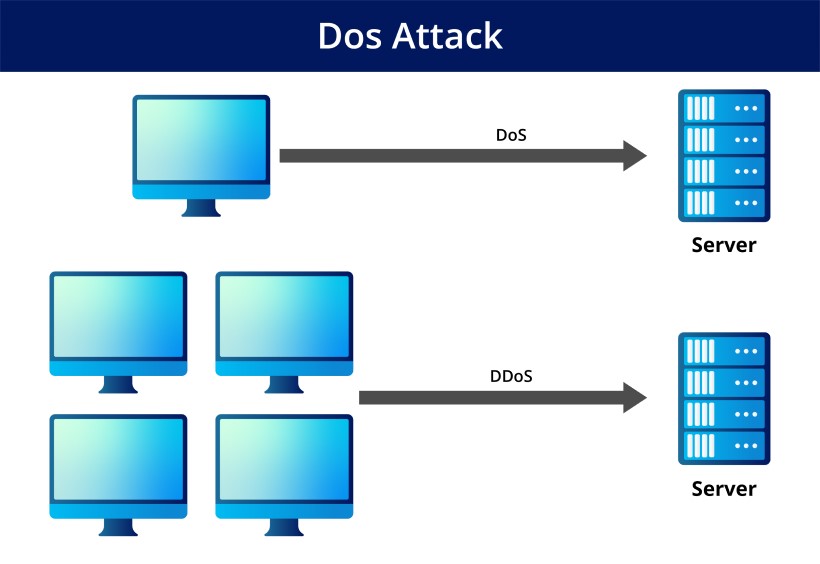
The goal of a DoS attack is to stop people who are allowed to use a machine or network from using it. This is done by flooding the target with questions and data that cause the system to crash. Employees, members, and consumers cannot use the system because their legitimate requests are overwhelmed by the attacker’s illicit activities.
DDoS attacks can be very costly for those affected. The attacks can be about the theft of data or assets. Enterprises, such as banks, shops, media companies, and government institutions, often target their web servers in these attacks.
TCP /IP Hijacking
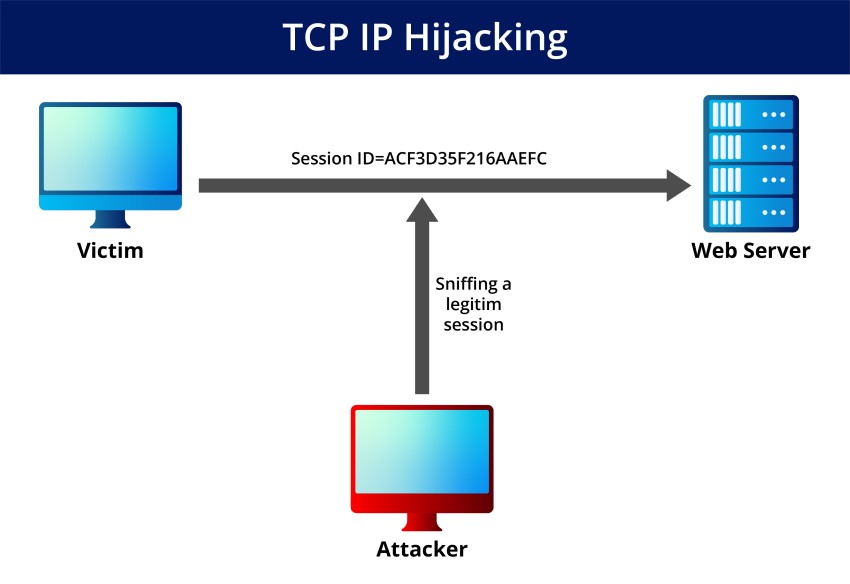
This type of attack is when a hacker takes over a session between two devices that are already communicating with each other. The attacker must be on the same network as the victim to carry out this attack.
When the attacker takes over the session, they can eavesdrop on the conversation and modify the data being exchanged. This attack often injects malware into a system or steals sensitive information.
SMB Relay Attack
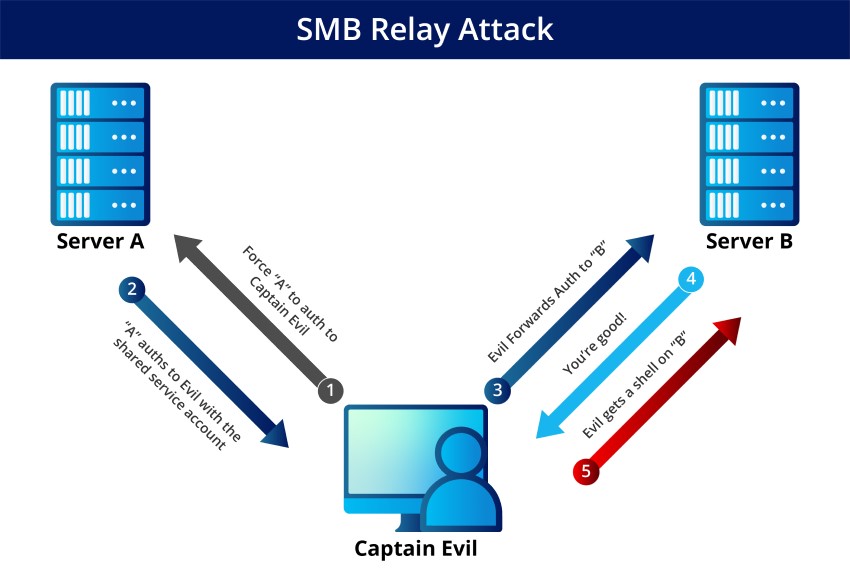
Server Message Block (SMB) Relay attacks are unfortunately common in corporations that still use NTLM Version 2 authentication. Cybercriminals can secretly forward sensitive data to other servers without getting caught by secretly listening in on network traffic.
Think about this problem from the perspective of an exemplary user and an evil hacker. The ideal scenario is when the actual person is trying to log in and authenticate themselves. When, instead of a valid user, a hacker tries to use stolen credentials by monitoring network traffic for them to gain access – there is no need for a password.
Recent advancements in hacking technology
Hackers are constantly finding new ways to access restricted information, which makes it evident that the Computer Fraud and Abuse Act needs to be updated. This law was created in the 1980s but has not been changed since 2011, meaning it is not responsive to more recent technological advances. CFAA must stay ahead of hackers by being regularly updated.
Lying on a dating profile may not seem important, but if the website’s terms of use are violated, you could be charged with hacking under the CFAA. This minor offense comes with a year in prison or a $100,000 fine.
Bypassing CAPTCHA Test
The CAPTCHA test determines whether a user is a human or a robot. It is commonly used for security purposes, like logging into your bank account. If caught trying to bypass the CAPTCHA, you could be charged with hacking and face up to 8 years in prison.
CAPTCHA is a website’s security measure to prevent bots from accessing them. It displays a picture that is difficult to decipher and to gain access, you must enter the letters and numbers displayed in a box below the image. However, hackers became so clever at hacking it that CAPTCHA had to become more complex, resulting in them being solved more frequently than humans. To combat this, reCAPTCHA was developed and involved looking at tiny squares and flagging them with a fire hydrant, bus, or crosswalk.
For the time being, reCAPTCHA is still active. However, it will not be long before automated machine-learning techniques can be discovered to bypass it.
Both reCAPTCHA and CAPTCHA were derived from the idea that it is feasible to identify humans from computers online in a low-cost, user-friendly, and quick manner. These questions force us to consider what makes us human and whether machines can duplicate that aspect. The obvious response is that we do not know because we have now jumped into the deep end of the philosophical pond.
So How Do You Stay Ahead of the Curve and Ensure Your Business or Website is Not Hacked?
Keep your software up to date
The most important thing is to keep your software up to date. This includes the operating system, any applications, and plugins. Outdated software is one of the most common ways hackers gain access to a system.
Another way to protect yourself is to Change your default username and password for any devices or accounts. Many people do not realize that the default username and password is easy to find online. Hackers know this and try these credentials before moving on to more complex methods.
Use two-factor authentication
Using two-factor authentication (2FA) is one of the best ways to protect your accounts from being hacked. 2FA adds an extra layer of security by requiring you to enter both a password and a code sent to your phone. This makes it much harder for hackers to access your account even if they have your password.
Disable Anonymous system access
Remote access attacks are on the rise, and taking steps to protect yourself is essential. Cybercriminals are becoming more sophisticated, so staying ahead of the curve is essential. Keeping your software up to date, using two-factor authentication, and disabling anonymous access are all effective ways to protect yourself. As technology advances, we will need to develop new ways to stay ahead of hackers in this cat-and-mouse game.
security
admin is a senior staff writer for Government Technology. She previously wrote for PYMNTS and The Bay State Banner, and holds a B.A. in creative writing from Carnegie Mellon. She’s based outside Boston.